Learning Outcomes
After completing this lesson, students will be able to:
i. Differentiate between short-distance and long-distance wireless communication technologies
ii. Identify the characteristics and applications of short-distance wireless communication
iii. Recognize the characteristics and applications of long-distance wireless communication
iv. Analyze the suitability of different wireless communication technologies for various applications
Introduction
Wireless communication, spanning a wide spectrum of technologies, encompasses a variety of methods for transmitting data over distances ranging from a few centimeters to thousands of kilometers. This lesson delves into the distinction between short-distance and long-distance wireless communications, exploring their unique characteristics and diverse applications.
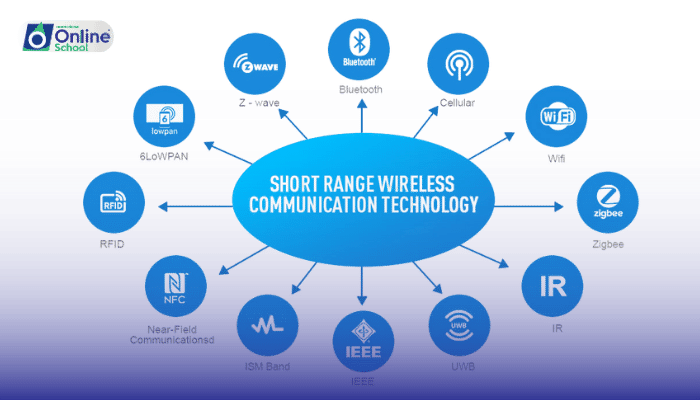
i. Short-Distance Wireless Communication: Bridging Short Distances
Short-distance wireless communication technologies operate over relatively short ranges, typically covering a few meters to a few hundred meters. These technologies are characterized by their high data transfer rates, low power consumption, and ease of implementation. Common examples of short-distance wireless communication include:
Bluetooth: Bluetooth, operating within a range of about 10 meters, is widely used for connecting peripherals like headphones, speakers, and wireless keyboards to smartphones and computers.
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11): Wi-Fi, providing internet access and data sharing within local area networks (LANs), has a range of up to 100 meters, depending on environmental factors.
Near Field Communication (NFC): NFC, with a range of a few centimeters, facilitates close-range data transfer, such as contactless payments or pairing devices.
ii. Long-Distance Wireless Communication: Spanning Vast Distances
Long-distance wireless communication technologies, unlike their short-distance counterparts, are designed to transmit data over vast distances, ranging from kilometers to thousands of kilometers. These technologies are characterized by their ability to cover large areas, their resilience to environmental factors, and their suitability for applications requiring wide coverage. Examples of long-distance wireless communication include:
Cellular Networks: Cellular networks, utilizing cell towers, provide mobile voice and data services over wide geographical areas, covering entire cities, countries, and even continents.
Satellite Communication: Satellite communication, using satellites orbiting the Earth, enables data transmission over long distances, connecting remote areas and providing communication services beyond terrestrial networks.
Radio Broadcasting: Radio broadcasting, utilizing radio waves, transmits audio, video, and data content over vast distances, reaching a wide audience through radio receivers.
iii. Applications: Matching Technology to Needs
The choice of wireless communication technology depends on the specific application and the required range, data transfer rate, and cost considerations. Short-distance technologies are suitable for connecting devices within a limited area, while long-distance technologies are ideal for spanning large distances and providing coverage over wide geographical regions.
Short-distance and long-distance wireless communication technologies have revolutionized the way we communicate, enabling seamless data exchange, mobility, and a wide range of applications. Understanding the characteristics and applications of these technologies is crucial for selecting the most appropriate solution for specific communication needs. As technology continues to evolve, wireless communication is poised to play an even more significant role in connecting the world and shaping our future.